We are excited to announce this major release of auditing tool Lynis. Several big changes have been made to core functions of Lynis. These changes are the next of simplification improvements we made. There is a risk of breaking your existing configuration.
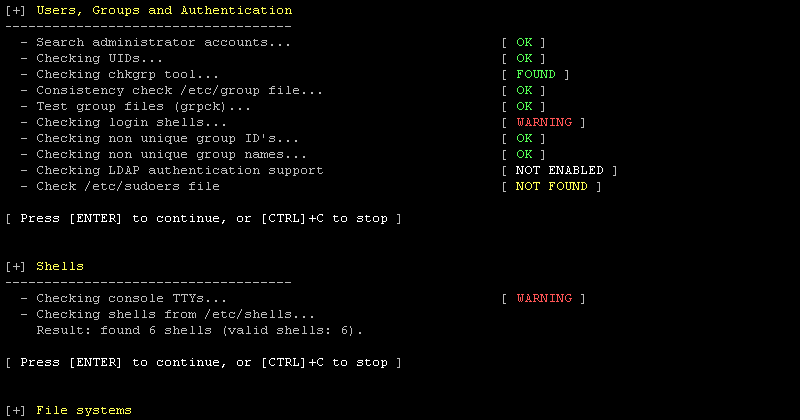
Lynis is an open source security auditing tool. Used by system administrators, security professionals, and auditors, to evaluate the security defenses of their Linux and UNIX-based systems. It runs on the host itself, so it performs more extensive security scans than vulnerability scanners.

- AIX
- FreeBSD
- HP-UX
- Linux
- Mac OS
- NetBSD
- OpenBSD
- Solaris
- and others
It even runs on systems like the Raspberry Pi and several storage devices!
Installation optional
Lynis is light-weight and easy to use. Installation is optional: just copy it to a system, and use “./lynis audit system” to start the security scan. It is written in shell script and released as open source software (GPL).
- Determine operating system
- Search for available tools and utilities
- Check for Lynis update
- Run tests from enabled plugins
- Run security tests per category
- Report status of security scan
- Security auditing
- Compliance testing (e.g. PCI, HIPAA, SOx)
- Vulnerability detection and scanning
- System hardening
- Best practices
- CIS
- NIST
- NSA
- OpenSCAP data
- Vendor guides and recommendations (e.g. Debian Gentoo, Red Hat)
Lynis Plugins
Plugins enable the tool to perform additional tests. They can be seen as an extension (or add-on) to Lynis, enhancing its functionality. One example is the compliance checking plugin, which performs specific tests only applicable to some standard.
Changelog
Upgrade note
Lynis 2.6.5 (2018-06-26)Tests:
——
* [MAIL-8804] – Exim configuration test
* [NETW-2704] – Use FQDN to test status of a nameserver instead of own IP address
* [SSH-7402] – Improved test to allow configurations with a Match block
Lynis 2.6.4 (2018-05-02)
Changes:
——–
* Several contributions merged, including grammar improvements
* Initial support for Ubuntu 18.04 LTS
* Small enhancements for usage
Tests:
——
* [AUTH-9308] – Made ‘sulogin’ more generic for systemd rescue shell
* [DNS-1600] – Initial work on DNSSEC validation testing
* [NETW-2704] – Added support for local resolver 127.0.0.53
* [PHP-2379] – Suhosin test disbled
* [SSH-7408] – Removed ‘DELAYED’ from OpenSSH Compression setting
* [TIME-3160] – Improvements to detect step-tickers file and entries











Add Comment