[sc name=”ad_1″]
The United States’ National Security Agency (NSA) is planning to release its internally developed reverse engineering tool for free at the upcoming RSA security conference 2019 that will be held in March in San Francisco.
The existence of the framework, dubbed GHIDRA, was first publicly revealed by WikiLeaks in CIA Vault 7 leaks, but the tool once again came to light after Senior NSA Adviser Robert Joyce announced to publicly release the tool for free in his RSA Conference session description.
Reverse engineering tool is a disassembler, for example, IDA-Pro, that help researchers identify certain portions of a program to see how they work by reading information like its processor instructions, instruction lengths, and more.
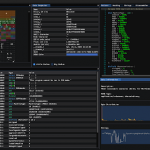
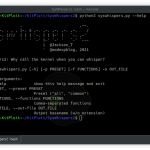
GHIDRA is a Java-based reverse engineering framework that features a graphical user interface (GUI) and has been designed to run on a variety of platforms including Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems, and also supports a variety of processor instruction sets.
The toolkit can also be used to analyze binary files used by programs, including malware, for all major operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Linux as well as mobile platforms such as Android and iOS.
A synopsis for Joyce’s presentation notes that “the Ghidra platform includes all the features expected in high-end commercial tools, with new and expanded functionality NSA uniquely developed, and will be released for free public use at RSA.”
According to the Vault 7 documents, GHIDRA was initially developed by the NSA in the early 2000s, and a Reddit user named hash_define who claimed to have had access to GHIDRA said that the tool had been shared with several other US government agencies in past few years.
While there is no such announcement that the NSA is planning to open source GHIDRA, some believe the agency will also publish GHIDRA source code on NSA’s code repository hosted by Github where it has already released 32 projects, so that the open source community can help maintain it for free.











Add Comment