ElasticIntel is serverless, low cost, threat intel aggregation for enterprise or personal use, backed by ElasticSearch. It is an alternative to expensive threat intel aggregation platforms which ingest the same data feeds you could get for free. ElasticIntel is designed to provide a central, scalable and easily queryable repository for threat intelligence of all types. Utilizes amazon services to allow for minimal support needs while maintaining scalability and resilience and performance. (aws lambda, elasticsearch, s3, sns)
Features
- Serverless – No maintenance required
- Scalable (all services scale via AWS)
- High performance API – API can be used to run extremely high volume queries
- Flexible – Feeds can be added via simple json feed configuration
- Extensible – written in python and extended by new modules
- Cost-effective – Pay only for the backend services – don’t worry about API limits
- Automated Deployment – platform can be deployed from a single command
- Works “out of the box” – comes pre-configured with 30+ opensource intel feeds
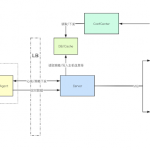
Architecture
- Feed Scheduler lambda – The feed scheduler lambda runs once an hour, just like a cron job. It downloads the configurations for all feeds, checks their scheduled download times and puts a download job into an sns queue a feed needs to be downloaded
- Ingest Feed Lambda – The ingest lambda is triggered by messages arriving to an sns topic. When a message arrives, the ingest lamda reads the message, parses out the information about the intel feed and downloads the feed itself. Once downloaded, the ingest lambda stores a copy of the feed in s3 and then parses out the data in the feed. Once the data is parsed, the ingest lambda puts the data into the intel index in elasticsearch for easy querying.
- intel objects define in set of values (json)
- intel feed objects define the feed itself (url, type(xml, csv, json), schedule)
- intel feeds may be easily added simply by defining a new feed configuration in the feeds directory.
- for API-based intel feeds, modules may be easily added in the form of python scripts and imported into the main feed manager
feed ingestion is done via a series of lambdas
- Feed scheduler:
- the scheduler lambda runs once an hours, reads the various config files and determines if any feeds need to be pulled in
- If a feed is determined to need refreshing, the scheduler lambda launches a new lambda to pull down that feed
Feed ingestion
feeds are ingested through the ingestfeed lambda function. this function is passed a event containing a feed dictionary, as well as the ES index where the indicators from the feed will be stored.
This function then reads the feed dictionary, downloads the appropriate data from the feed url, saves that data to an s3 bucket as a timestamped file, parses that data into intel objects and finally indexes the feed data in teh specified ES index
Elasticsearch
It is important to note that intel is not unique. Each feed is queried daily and some intel may appear in a feed across multiple days. This is by designed, to allow a history view of indicators.
However, this may not be your default expected behavior when querying against the data, so it is important to realize that the number of times an indicator shows up may not be indicative of a high threat score.
Requirements note
if pip3 fails on crypto install, make sure libssl-dev is installed (sudo apt install libssl-dev)
Issues
- Elasticsearch, while extremely powerful in its query language, has a very high barrier to entry. For actively slicing and dicing data, piping or copying data to splunk may yield more maleable data.
- Queries are best written in the developer tools section of kibana













Add Comment