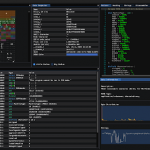
The GOSINT framework is a project used for collecting, processing, and exporting high quality indicators of compromise (IOCs). GOSINT allows a security analyst to collect and standardize structured and unstructured threat intelligence. Applying threat intelligence to security operations enriches alert data with additional confidence, context, and co-occurrence. This means that you apply research from third parties to security event data to identify similar, or identical, indicators of malicious behavior. The framework is written in Go with a JavaScript frontend.
There is already so much open source [threat] intelligence (OSINT) available on the web, but no easy way to collect and filter through it to find useful info. GOSINT aggregates, validates, and sanitizes indicators for consumption by other tools like CRITs, MISP, or directly into log management systems or SIEM. While the threat intelligence sharing community matures, GOSINT will adapt to support additional export formats and indicator sharing protocols.
You can think of GOSINT as a transfer station for threat indicators. The software allows threat intelligence analysts to judge whether an indicator is worthy of tracking or if it should be rejected. This decision making step is crucial in managing any set of threat indicators. Vetting by both a human analyst and GOSINT itself improves the quality of indicators threat detection efficacy. There is no limit to the number of indicator sources you can add.
As part of the vetting process, currently GOSINT can take several actions to provide additional context to indicators in the pre-processing phase. An analyst can run indicators through Cisco Umbrella, ThreatCrowd, VirusTotal, and other sources. The information returned from these services can help an analyst reach a verdict on the value of the indicator, as well as tag the indicator with additional context that might be used later on in the analysis pipeline.
There is also a “Recipe Manager” that allows you to perform multiple operations on threat indicators from various sources. Say for example you want to always compare sha256 hash values from a favorite twitter feed with the VirusTotal API, and if there’s greater than 3 detections, add the hash indicators to production. The manager offers several configurable options to allow analysts to speed up their indicator processing and enriching.
GOSINT also has another useful feature with its “Ad Hoc Input” option. This allows an analyst to point GOSINT at a URL and fetch any or all indicators available. For example, if an analyst reads a blog about a particular malware campaign or malware analysis, GOSINT can crawl the blog for indicators and import them for pre-processing. This ad-hoc method allows analysts to quickly import indicators from content that cannot be automatically subscribed to, or has intermittent data available.
Installation
It is recommended that GOSINT be installed on a GNU/Linux system with the latest version of the Go language available.
Quick Installation
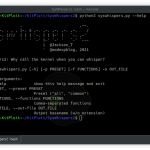
- Option 1: Bash script installThis process will allow GOSINT to be installed via pre-configured install scripts. Note that these scripts were tested on a 64-bit version of 16.04 Ubuntu, and a 32-bit version of 14.04 Ubuntu.
- Navigate to
bash-installdirectory in the repository - Execute
sudo bash 1-install.shand enterYto all confirmation prompts. - At the conclusion, the GOSINT binary will be running. If all went well, open your web browser and navigate to http://localhost/ to view the GOSINT dashboard.
- Navigate to
- Option 2: Docker
- A community member has developed a version of GOSINT that runs on Docker as viewable here: https://github.com/Jsitech/DockerFiles/tree/master/gosint
- You can pull this from the Docker Hub as:
docker pull jsitech/gosint - Note: This repository may not have the latest updates of the official repository. To ensure you have the latest code, either use the pre-configured installation bash scripts (as above) or look below for the more manual process.
Manual Installation
The following was prepared specifically for Ubuntu Server 16.04.2 LTS.
Pre-Requisites
GOSINT requires
- A working and up to date Go environment
- Mongo DB (Community Edition is ok)
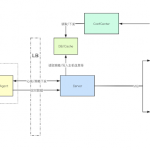
- A reverse proxy/web server (NGINX preferred)
- PHP
You can use your preferred package manager to install most of these environments and applications. For aptitude:
sudo apt-get install mongodb php-fpm nginx git
- Install MongoDB and ensure it is ONLY listening on your local loopback interface (127.0.0.1/localhost) if you are running it on the same host as GOSINT.
- Allowing your database to listen on any externally facing ports is a security risk, and should not be done without proper precautions taken to prevent unauthorized access.
- You can use aptitude to install an older version with the command
sudo apt-getinstall mongodb, or you can follow the instructions at https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/tutorial/install-mongodb-on-ubuntu/ to install a more up to date version from the MongoDB repositories.
- Install PHP (v5 or higher) and verify the installation was successful.
- Install NGINX (or your preferred web server).
- You will need to configure NGINX to listen on a public interface at a port you specify.
- It is recommended that you install a valid certificate for HTTPS and enable some form of authorization (local auth or LDAP) to prevent unauthorized access to GOSINT.
- Please find the base nginx configuration file at NGINX Configuration











Add Comment