[sc name=”ad_1″]
FestIn is a tool for discovering open S3 Buckets starting from a domains.
It perform a lot of test and collects information from:
- DNS
- Web Pages (Crawler)
- S3 bucket itself (like S3 redirections)
Why Festin
There’s a lot of S3 tools for enumeration and discover S3 bucket. Some of them are great but anyone have a complete list of features that Festin has.
Main features that does Festin great:
- Various techniques for finding buckets: crawling, dns crawling and S3 responses analysis.
- Proxy support for tunneling requests.
- AWS credentials are not needed.
- Works with any S3 compatible provider, not only with AWS.
- Allows to configure custom DNS servers.
- Integrated high performance HTTP crawler.
- Recursively search and feedback from the 3 engines: a domain found by dns crawler is send to S3 and Http Crawlers analyzer and the same for the S3 and Crawler.
- Works as ‘watching’ mode, listening for new domains in real time.
- Save all of the domains discovered in a separate file for further analysis.
- Allow to download bucket objects and put then in a FullText Search Engine (Redis Search) automatically, indexing the objects content allowing powerful search further.
- Limit the search for specific domain/s.
Install
Using Python
Python 3.8 of above needed!$ pip install festin
$ festin -hUsing Docker
$ docker run --rm -it cr0hn/festin -hFull options
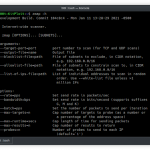
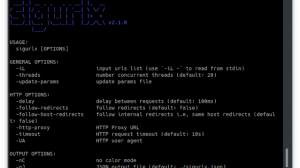
$ festin -h
usage: __main__.py [-h] [--version] [-f FILE_DOMAINS] [-w] [-c CONCURRENCY] [--no-links] [-T HTTP_TIMEOUT] [-M HTTP_MAX_RECURSION] [-dr DOMAIN_REGEX] [-rr RESULT_FILE] [-rd DISCOVERED_DOMAINS] [-ra RAW_DISCOVERED_DOMAINS]
[--tor] [--debug] [--no-print] [-q] [--index] [--index-server INDEX_SERVER] [-dn] [-ds DNS_RESOLVER]
[domains [domains ...]]
Festin - the powered S3 bucket finder and content discover
positional arguments:
domains
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--version show version
-f FILE_DOMAINS, --file-domains FILE_DOMAINS
file with domains
-w, --watch watch for new domains in file domains '-f' option
-c CONCURRENCY, --concurrency CONCURRENCY
max concurrency
HTTP Probes:
--no-links extract web s ite links
-T HTTP_TIMEOUT, --http-timeout HTTP_TIMEOUT
set timeout for http connections
-M HTTP_MAX_RECURSION, --http-max-recursion HTTP_MAX_RECURSION
maximum recursison when follow links
-dr DOMAIN_REGEX, --domain-regex DOMAIN_REGEX
only follow domains that matches this regex
Results:
-rr RESULT_FILE, --result-file RESULT_FILE
results file
-rd DISCOVERED_DOMAINS, --discovered-domains DISCOVERED_DOMAINS
file name for storing new discovered after apply filters
-ra RAW_DISCOVERED_DOMAINS, --raw-discovered-domains RAW_DISCOVERED_DOMAINS
file name for storing any domain without filters
Connectivity:
--tor Use Tor as proxy
Display options:
--debug enable debug mode
--no-print doesn't print results in sc reen
-q, --quiet Use quiet mode
Redis Search:
--index Download and index documents into Redis
--index-server INDEX_SERVER
Redis Search ServerDefault: redis://localhost:6379
DNS options:
-dn, --no-dnsdiscover
not follow dns cnames
-ds DNS_RESOLVER, --dns-resolver DNS_RESOLVER
comma separated custom domain name serversUsage
Configure search domains
By default FestIn accepts a start domain as command line parameter:
> festin mydomain.comBut you also cat setup an external file with a list of domains:
> cat domains.txt
domain1.com
domain2.com
domain3.com
> festin -f domains.txt Concurrency
FestIn performs a lot of test for a domain. Each test was made concurrently. By default concurrency is set to 5. If you want to increase the number of concurrency tests you must set the option -c
> festin -c 10 mydomain.com Be carefull with the number of concurrency test or "alarms" could raises in some web sites.HTTP Crawling configuration
FestIn embed a small crawler to discover links to S3 buckets. Crawler accepts these options:
- Timeout (
-Tor--http-timeout): configure a timeout for HTTP connections. If website of the domain you want to analyze is slow, we recommend to increase this value. By default timeout is 5 seconds. - Maximum recursion (
-Hor--http-max-recursion): this value setup a limit for crawling recursion. OtherwiseFestInwill scan all internet. By default this value is 3. It means that only will follow: domain1.com -> http://feedproxy.google.com/~r/PentestTools/~3/IsCkuOcHH-s/festin-s3-bucket-weakness-discovery.html -> domain2.com -> http://feedproxy.google.com/~r/PentestTools/~3/IsCkuOcHH-s/festin-s3-bucket-weakness-discovery.html -> domain3.com -> http://feedproxy.google.com/~r/PentestTools/~3/IsCkuOcHH-s/festin-s3-bucket-weakness-discovery.html -> Maximum recursion reached. Stop - Limit domains (
-dror--domain-regex): set this option to limit crawler to these domains that matches with this regex.
Example:
> festin -T 20 -H 8 -dr *mydomain* mydomain.com Manage results
When FestIn runs it discover a lot of useful information. Not only about S3 buckets, also for other probes we could do. For example:
After we use FestIn we can use discovered information (domains, links, resources, other buckets…) as input of other tools, like nmap.
For above reason FestIn has 3 different modes to store discovered information and we can combine them:
FestInresult file (-rror--result-file): this file contains one JSON per line with buckets found by them. Each JSON includes: origin domain, bucket name and the list of objects for the bucket.- Filtered discovered domains file (
-rdor--discovered-domains): this file contains one domain per line. These domains are discovered by the crawler, dns or S3 probes but only are stored these domains that matches with user and internal filters. - Raw discovered domains file (
-raor--raw-discovered-domains): this file contains all domains, one per line, discovered byFestInwithout any filter. This option is useful for post-processing and analyzing.
Example:
> festin -rr festin.results -rd discovered-domains.txt -ra raw-domains.txt mydomain.txt And, chaining with Nmap:
> festin -rd domains.txt && nmap -Pn -A -iL domains.txt -oN nmap-domains.txt Proxy usage
FestIn embeds the option --tor. By using this parameter you need local Tor proxy running at port 9050 at 127.0.0.1.
> tor &
> festin --tor mydomain.com DNS Options
Some tests made by FestIn involves DNS. It support these options:
- Disable DNS discovery (
-dnor--no-dnsdiscover) - Custom DNS server (
-dsor--dns-resolver): setup custom DNS server. If you plan to perform a lot of tests you should use a different DNS server like you use to your browser.
Example:
> festin -ds 8.8.8.8 mydomain.com Full Text Support
FestIn not only can discover open S3 buckets. It also can download all content and store them in a Full Text Search Engine. This means that you can perform Full Text Queries to the content of the bucket!
FestIn uses as Full Text Engine the Open Source project Redis Search.
This feature has two options:
- Enable indexing (
--index): to enable the indexing to the search engine you must setup this flag. - Redis Search config (
--index-server): you only need to setup this option if your server is running in a different IP/Port that: localhost:6379.
Example:
> docker run --rm -p 6700:6379 redislabs/redisearch:latest -d
> festin --index --index-server redis://127.0.0.1:6700 mydomain.comPay attention to option `--index-server` is must has the prefix **redis://** Running as a service (or watching mode)
Some times we don’t want to stop FestIn and launch them some times when we have a new domain to inspect or any external tool discovered new domains we want to check.
FestIn supports watching mode. This means that FestIn will start and listen for new domains. The way to “send” new domains to FestIn is by domains file. It monitor this file for changes.
This feature is useful to combine FestIn with other tools, like dnsrecon
Example:
> festin --watch -f domains.txt In a different terminal we can write:
> echo "my-second-domain.com" >> domains.txt
> echo "another-domain.com" >> domains.txt Each new domain added to domains.txt will wakeup FestIn.
Example: Mixing FesTin + DnsRecon
Using DnsRecon
The domain chosen for this example is target.com.
Step 1 – Run dnsrecon with desired options against target domain and save the output
> dnsrecon -d target.com -t crt -c target.com.csvWith this command we are going to find out other domains related to target.com. This will help to maximize our chances of success.
Step 2 – Prepare the previous generated file to feed FestIn
> tail -n +2 target.com.csv | sort -u | cut -d "," -f 2 >> target.com.domainsWith this command we generate a file with one domain per line. This is the input that FestIn needs.
Step 3 – Run FestIn with desired options and save output
> festin -f target.com.domains -c 5 -rr target.com.result.json --tor -ds 212.166.64.1 >target.com.stdout 2>target.com.stderrIn this example the resulting files are:
- target.com.result.json – Main result file with one line per bucket found. Each line is a JSON object.
- target.com.stdout – The standard output of festin command execution
- target.com.stderr – The standard error of festin command execution
In order to easy the processing of multiple domains, we provide a simple script examples/loop.sh that automatize this.
Using FestIn with DnsRecon results
Run against target.com with default options and leaving result to target.com.result file:
> festin target.com -rr target.com.result.json Run against target.com using tor proxy, with concurrency of 5, using DNS 212.166.64.1 for resolving CNAMEs and leaving result to target.com.result file:
> festin target.com -c 5 -rr target.com.result.json --tor -ds 212.166.64.1 F.A.Q.
Q: AWS bans my IP A:
When you perform a lot of test against AWS S3, AWS includes your IP in a black list. Then each time you want to access to any S3 bucket with FestIn of with your browser will be blocked.
We recommend to setup a proxy when you use FestIn.
Who uses FestIn
MrLooquer
They analyze and assess your company risk exposure in real time. Website
[sc name=”ad-in-article”]











Add Comment