Wifiphisher is a security tool that mounts automated victim-customized phishing attacks against WiFi clients in order to obtain credentials or infect the victims with malwares. It is primarily a social engineering attack that unlike other methods it does not include any brute forcing. It is an easy way for obtaining credentials from captive portals and third party login pages (e.g. in social networks) or WPA/WPA2 pre-shared keys.
After achieving a man-in-the-middle position using the Evil Twin or KARMA attack, Wifiphisher redirects all HTTP requests to an attacker-controlled phishing page. From the victim’s perspective, the attack makes use in three phases:
- Victim is being deauthenticated from her access point. Wifiphisher continuously jams all of the target access point’s wifi devices within range by forging “Deauthenticate” or “Disassociate” packets to disrupt existing associations.
- Victim joins a rogue access point. Wifiphisher sniffs the area and copies the target access point’s settings. It then creates a rogue wireless access point that is modeled by the target. It also sets up a NAT/DHCP server and forwards the right ports. Consequently, because of the jamming, clients will eventually start connecting to the rogue access point. After this phase, the victim is MiTMed.
- Victim is being served a realistic specially-customized phishing page. Wifiphisher employs a minimal web server that responds to HTTP & HTTPS requests. As soon as the victim requests a page from the Internet, wifiphisher will respond with a realistic fake page that asks for credentials or serves malwares. This page will be specifically crafted for the victim. For example, a router config-looking page will contain logos of the victim’s vendor. The tool supports community-built templates for different phishing scenarios.

Usage
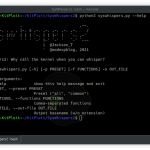
Run the tool by typing wifiphisher or python bin/wifiphisher (from inside the tool’s directory).
By running the tool without any options, it will find the right interfaces and interactively ask the user to pick the ESSID of the target network (out of a list with all the ESSIDs in the around area) as well as a phishing scenario to perform.
wifiphisher -aI wlan0 -jI wlan4 -p firmware-upgrade
Use wlan0 for spawning the rogue Access Point and wlan4 for DoS attacks. Select the target network manually from the list and perform the “Firmware Upgrade” scenario.
Useful for manually selecting the wireless adapters. The “Firware Upgrade” scenario is an easy way for obtaining the PSK from a password-protected network.
wifiphisher --essid CONFERENCE_WIFI -p plugin_update -pK s3cr3tp4ssw0rd
Automatically pick the right interfaces. Target the Wi-Fi with ESSID “CONFERENCE_WIFI” and perform the “Plugin Update” scenario. The Evil Twin will be password-protected with PSK “s3cr3tp4ssw0rd”.
Useful against networks with disclosed PSKs (e.g. in conferences). The “Plugin Update” scenario provides an easy way for getting the victims to download malicious executables (e.g. malwares containing a reverse shell payload).
wifiphisher --nojamming --essid "FREE WI-FI" -p oauth-login
Do not target any network. Simply spawn an open Wi-Fi network with ESSID “FREE WI-FI” and perform the “OAuth Login” scenario.
Useful against victims in public areas. The “OAuth Login” scenario provides a simple way for capturing credentials from social networks, like Facebook.
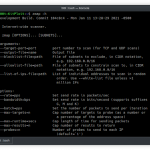
Following are all the options along with their descriptions (also available with wifiphisher -h):
| Short form | Long form | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| -h | –help | show this help message and exit |
| -s SKIP | –skip SKIP | Skip deauthing this MAC address. Example: -s 00:11:BB:33:44:AA |
| -jI JAMMINGINTERFACE | –jamminginterface JAMMINGINTERFACE | Manually choose an interface that supports monitor mode for deauthenticating the victims. Example: -jI wlan1 |
| -aI APINTERFACE | –apinterface APINTERFACE | Manually choose an interface that supports AP mode for spawning an AP. Example: -aI wlan0 |
| -t TIMEINTERVAL | –timeinterval TIMEINTERVAL | Choose the time interval between DEAUTH packets being sent |
| -dP DEAUTHPACKETS | –deauthpackets DEAUTHPACKETS | Choose the number of packets to send in each deauth burst. Default value is 1; 1 packet to the client and 1 packet to the AP. Send 2 deauth packets to the client and 2 deauth packets to the AP: -dP 2 |
| -d | –directedonly | Skip the deauthentication packets to the broadcast address of the access points and only send them to client/AP pairs |
| -nJ | –nojamming | Skip the deauthentication phase. When this option is used, only one wireless interface is required |
| -e ESSID | –essid ESSID | Enter the ESSID of the rogue Access Point. This option will skip Access Point selection phase. Example: –essid ‘Free WiFi’ |
| -p PHISHINGSCENARIO | –phishingscenario PHISHINGSCENARIO | Choose the phishing scenario to run.This option will skip the scenario selection phase. Example: -p firmware_upgrade |
| -pK PRESHAREDKEY | –presharedkey PRESHAREDKEY | Add WPA/WPA2 protection on the rogue Access Point. Example: -pK s3cr3tp4ssw0rd |
Requirements
Following are the requirements for getting the most out of Wifiphisher:
- Kali Linux. Although people have made Wifiphisher work on other distros, Kali Linux is the officially supported distribution, thus all new features are primarily tested on this platform.
- One wireless network adapter that supports AP mode. Drivers should support netlink.
- One wireless network adapter that supports Monitor mode and is capable of injection. Again, drivers should support netlink. If a second wireless network adapter is not available, you may run the tool with the –nojamming option. This will turn off the de-authentication attack though.
Installation
To install the latest development version type the following commands:
git clone https://github.com/sophron/wifiphisher.git # Download the latest revision cd wifiphisher # Switch to tool's directory sudo python setup.py install # Install any dependencies (Currently, hostapd, PyRIC, jinja2)
Download Wifiphisher











Add Comment