sslh accepts connections on specified ports, and forwards them further based on tests performed on the first data packet sent by the remote client. Probes for HTTP, SSL, SSH, OpenVPN, tinc, XMPP are implemented, and any other protocol that can be tested using a regular expression, can be recognised. A typical use case is to allow serving several services on port 443 (e.g. to connect to SSH from inside a corporate firewall, which almost never block port 443) while still serving HTTPS on that port. Hence sslh acts as a protocol demultiplexer, or a switchboard. Its name comes from its original function to serve SSH and HTTPS on the same port.
Compile and install
Dependencies
sslh uses libconfig and libwrap.
For Debian, these are contained in packages libwrap0-dev and libconfig8-dev.
Compilation
After this, the Makefile should work:
make install
There are a couple of configuration options at the beginning of the Makefile:
USELIBWRAPcompiles support for host access control (seehosts_access(3)), you will needlibwrapheaders and library to compile (libwrap0-devin Debian).USELIBCONFIGcompiles support for the configuration file. You will needlibconfigheaders to compile (libconfig8-devin Debian).
Binaries
The Makefile produces two different executables: sslh-fork and sslh-select:
sslh-forkforks a new process for each incoming connection. It is well-tested and very reliable, but incurs the overhead of many processes.
If you are going to usesslhfor a “small” setup (less than a dozen ssh connections and a low-traffic https server) thensslh-forkis probably more suited for you.sslh-selectuses only one thread, which monitors all connections at once. It is more recent and less tested, but only incurs a 16 byte overhead per connection. Also, if it stops, you’ll lose all connections, which means you can’t upgrade it remotely.
If you are going to usesslhon a “medium” setup (a few thousand ssh connections, and another few thousand ssl connections),sslh-selectwill be better.
If you have a very large site (tens of thousands of connections), you’ll need a vapourware version that would use libevent or something like that.
Installation
- In general:
make cp sslh-fork /usr/local/sbin/sslh cp basic.cfg /etc/sslh.cfg vi /etc/sslh.cfg - For Debian:
cp scripts/etc.init.d.sslh /etc/init.d/sslh
You might need to create links in /etc/rc.d so that the server start automatically at boot-up, e.g. under Debian:
update-rc.d sslh defaults
Configuration
If you use the scripts provided, sslh will get its configuration from /etc/sslh.cfg. Please refer to example.cfg for an overview of all the settings. A good scheme is to use the external name of the machine in listen, and bind httpd tolocalhost:443 (instead of all binding to all interfaces): that way, HTTPS connections coming from inside your network don’t need to go through sslh, and sslh is only there as a frontal for connections coming from the internet.
Note that ‘external name’ in this context refers to the actual IP address of the machine as seen from your network, i.e. that that is not 127.0.0.1 in the output of ifconfig(8).
Libwrap support
Sslh can optionnaly perform libwrap checks for the sshd service: because the connection to sshdwill be coming locally from sslh, sshd cannot determine the IP of the client.
OpenVPN support
OpenVPN clients connecting to OpenVPN running with -port-share reportedly take more than one second between the time the TCP connexion is established and the time they send the first data packet. This results in sslh with default settings timing out and assuming an SSH connexion. To support OpenVPN connexions reliably, it is necessary to increase sslh‘s timeout to 5 seconds.
Instead of using OpenVPN’s port sharing, it is more reliable to use sslh‘s --openvpn option to getsslh to do the port sharing.
Using proxytunnel with sslh
If you are connecting through a proxy that checks that the outgoing connection really is SSL and rejects SSH, you can encapsulate all your traffic in SSL using proxytunnel (this should work withcorkscrew as well). On the server side you receive the traffic with stunnel to decapsulate SSL, then pipe through sslh to switch HTTP on one side and SSL on the other.
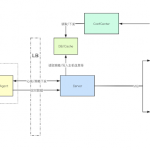
In that case, you end up with something like this:
ssh -> proxytunnel -e ----[ssh/ssl]---> stunnel ---[ssh]---> sslh --> sshd Web browser -------------[http/ssl]---> stunnel ---[http]--> sslh --> httpd
Configuration goes like this on the server side, using stunnel3:
stunnel -f -p mycert.pem -d thelonious:443 -l /usr/local/sbin/sslh -- \
sslh -i --http localhost:80 --ssh localhost:22
- stunnel options:
-ffor foreground/debugging-pfor specifying the key and certificate-dfor specifying which interface and port we’re listening to for incoming connexions-lsummonssslhin inetd mode.
- sslh options:
-ifor inetd mode--httpto forward HTTP connexions to port 80, and SSH connexions to port 22.
Transparent proxy support
On Linux and FreeBSD you can use the --transparent option to request transparent proying. This means services behind sslh (Apache, sshd and so on) will see the external IP and ports as if the external world connected directly to them. This simplifies IP-based access control (or makes it possible at all).
Linux:
sslh needs extended rights to perform this: you’ll need to give it CAP_NET_ADMIN capabilities (see appropriate chapter) or run it as root (but don’t do that). The firewalling tables also need to be adjusted as follow. The example connects to HTTPS on 4443 — adapt to your needs ; I don’t think it is possible to have httpd listen to 443 in this scheme — let me know if you manage that:
# iptables -t mangle -N SSLH # iptables -t mangle -A OUTPUT --protocol tcp --out-interface eth0 --sport 22 --jump SSLH # iptables -t mangle -A OUTPUT --protocol tcp --out-interface eth0 --sport 4443 --jump SSLH # iptables -t mangle -A SSLH --jump MARK --set-mark 0x1 # iptables -t mangle -A SSLH --jump ACCEPT # ip rule add fwmark 0x1 lookup 100 # ip route add local 0.0.0.0/0 dev lo table 100
Tranparent proxying with IPv6 is similarly set up as follows:
# ip6tables -t mangle -N SSLH # ip6tables -t mangle -A OUTPUT --protocol tcp --out-interface eth0 --sport 22 --jump SSLH # ip6tables -t mangle -A OUTPUT --protocol tcp --out-interface eth0 --sport 4443 --jump SSLH # ip6tables -t mangle -A SSLH --jump MARK --set-mark 0x1 # ip6tables -t mangle -A SSLH --jump ACCEPT # ip -6 rule add fwmark 0x1 lookup 100 # ip -6 route add local ::/0 dev lo table 100
Note that these rules will prevent from connecting directly to ssh on the port 22, as packets coming out of sshd will be tagged. If you need to retain direct access to ssh on port 22 as well as through sslh, you can make sshd listen to 22 AND another port (e.g. 2222), and change the above rules accordingly.









Add Comment