[sc name=”ad_1″]
yet another dirbuster
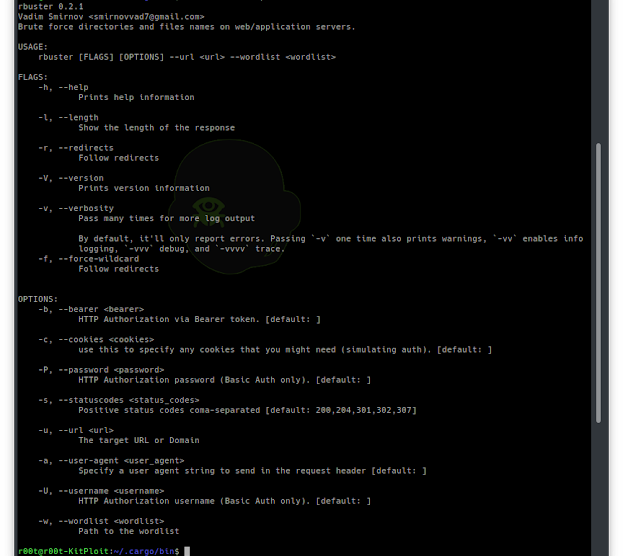
Common Command line options
-a <user agent string>– specify a user agent string to send in the request-c <http cookies>– use this to specify any cookies that you might need (simulating auth). header.-f– force processing of a domain with wildcard results.-l– show the length of the response.-r– follow redirects.-s <status codes>– comma-separated set of the list of status codes to be deemed a “positive” (default:200,204,301,302,307).-u <url/domain>– full URL (including scheme), or base domain name.-v– verbose output (show all results).-w <wordlist>– path to the wordlist used for brute forcing.-b <token>– HTTP Authorization via Bearer token.-P <password>– HTTP Authorization password (Basic Auth only, prompted if missing).-U <username>– HTTP Authorization username (Basic Auth only).
Install
cargo install rbusterInstall in kali
apt install libssl-dev pkg-config
cargo install rbusterExample
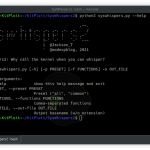
$ rbuster -w common.txt -u http://horriblesubs.info/Rbuster 0.1.0 Vadim Smirnov
=====================================================
Url/Domain : http://horriblesubs.info/
Wordlist : common.txt
Words : 4593
=====================================================
/thanks (Status: 301 Moved Permanently | Content-Length: 0)
/the (Status: 301 Moved Permanently | Content-Length: 0)
/ro (Status: 301 Moved Permanently | Content-Length: 0)
/robot (Status: 301 Moved Permanently | Content-Length: 0)
/robotics (Status: 301 Moved Permanently | Content-Length: 0)
/robots.txt (Status: 200 OK | Content-Length: 67)
[sc name=”ad-in-article”]










Add Comment