Seccubus automates regular vulnerability scans with various tools and aids security people in the fast analysis of its output, both on the first scan and on repeated scans.
On repeated scan delta reporting ensures that findings only need to be judged when they first appear in the scan results or when their output changes.
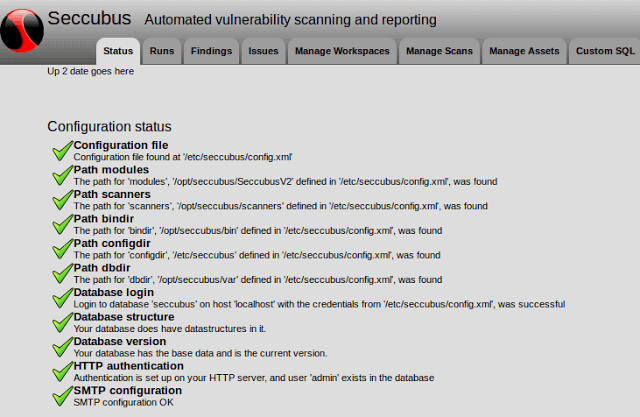
Seccubus 2.x is the only actively developed and maintained branch and all support for Seccubus V1 has officially been dropped.
Seccubus V2 works with the following scanners:
- Nessus
- OpenVAS
- Skipfish
- Medusa (local and remote)
- Nikto (local and remote)
- NMap (local and remote)
- OWASP-ZAP (local and remote)
- SSLyze
- Medusa
- Qualys SSL labs
- testssl.sh (local and remote)
For more information visit [www.seccubus.com]
Seccubus Docker container
Usage
Running a full stack (db/app/frontend) in a single container. And get an interactive shell
docker run -it seccubus/seccubus /bin/bashBy default the container holds a mysql server that runs and stores data locally. If you want data persistency there are two options:
Connect the container to a remote mysql/MariaDB database with environment viariables:
docker run -ti seccubus/seccubus -e DBHOST=dns.name.of.db.host \
-e DBPOSRT=3306 \
-e DBNAME=name.of.database \
-e DBUSER=db.username \
-e DBPASS=password \
/bin/bashOr, mount a data volume with a db directory on it
mkdir data
mmdir data/db
docker run -it seccubus/seccubus -v ($pwd)/data:/opt/seccubus/data /bin/bashPlease be aware that you can only run one container at a time if you mount a local directory on /var/lib/mysql.
Running a scan
Run the following command to start the scan ‘ssllabs’ in workspace ‘Example’ (this workspace is created by default if you use the local mysql database)
docker run -ti seccubus/seccubus scan Example ssllabsPlease be aware that you need soem data persistency here or the data will be stored in a local database that will be deleted whent he container terminates
Running a scheduler
You can run a docker container as a scheduler. This will make it run cron and allow your crontab to execute scans.You can populate the crontab by either placing a file called crontab in the /opt/seccubus/data volume or puting the lines of you crontab in evironement variables starting with CRON_
docker run -e "STACK=cron" -e "CRON_1=* 0 * * * bin/do-scan -w Example -s ssllabs" -ti seccubus/seccubusThis will spin up a container that executes scan ssllabs from workspace Example at midnight every night.
You can set the TZ vairable to control the timezone.
Controlling TLS certificates
The Seccubus container is TLS enabled by default. The environment variable TLS controls this behaviour. Of it is set to anything other then yes, TLS is turned off.
There are three ways to control the certificate:
- Do nothing : Self signed certificates will be generated for you
- Populate the variables TLSCERT and TLSKEY : The contents will be placed in /opt/seccubus/data/seccubus.pem and /opt/seccubus/data/seccubus.key and used
- Put the certificates in the files seccubus.pem and seccubus.key on a data volume and mount it on /opt/seccubus/data
Show this help message
docker run -ti seccubus/seccubus helpDefault command
If you don’t specify a command to docker run
docker run seccubus/seccubusThe web server access log and error log will be tailed to the screen.
Other options
You can set the following environment variables:
- STACK – Determines which part of the stack is run
- full – Run everything
- front – Start apache to serve the html/javascript frontend (this requires that the APIURL variable is set too)
- api – Start apache to serve the json api at / (starts MariaDB too if required)
- web – Start apache to serve both the html/javascript frontend and the json
- perl – Do not start apache, just use this container as an perl backend
- DBHOST, DBPORT, DBNAME, DBUSER, DBPASS – Database connection parameters
- If DBHOST/DBPORT are set to 127.0.0.1/3306 the local MariaDB instance is started
- APIURL – Path to the API url
- Set this if your set STACK to front to redirect the API calls to an alternative relative or absolute URL.
- BASEURI – Base URI for seccubus
- Server the application at the value provided
- SMTPSERVER – IP address or host name of an SMTP server to be used for notifications
- SMTPFROM – From address used in notifications
- TICKETURL_HEAD/TICKETURL_TAIL – If these are set ticket numberrs will be linked to this URL
- E.g. TICKERURL_HEAD = https://jira.example.com/projects/SECC/issues/
- TICKERURL_TAIL = ?filter=allopenissues
- Ticket SECC-666 would be linked to https://jira.example.com/projects/SECC/issues/SECC-666?filter=allopenissues
- SSHKEY1, SSHKEY2, SSHKEY3 .. SSHKEY9
- The content of this environment variable will stored in the file /opt/seccubus/.ssh/SSHKEY1 etc.
- You can use this mechanism to provide ssh keys that are used to start remote scans
- HTTP_AUTH_HEADER – Set the http authentication header
- If you are using something like OpenAM to authenticate your users, this allows you to set which http request header contains the user that OpenAM detected
- TZ – Set the timezone of the container
- TLS – Controls TLS behaviour
yesmeans TLS is on, otherwise TLS is off. TLS is on by default. - JIT_GROUP – Controls JIT provisioning of users
- CRON_MAIL_TO – Mail cron messages to this addres
- CRON_* – Add these lines to crontab in alphabetical order











Add Comment