[sc name=”ad_1″]
celerystalk helps you automate your network scanning/enumeration process with asynchronous jobs (aka tasks) while retaining full control of which tools you want to run.
- Configurable – Some common tools are in the default config, but you can add any tool you want
- Service Aware – Uses nmap/nessus service names rather than port numbers to decide which tools to run
- Scalable – Designed for scanning multiple hosts, but works well for scanning one host at a time
- VirtualHosts – Supports subdomain recon and virtualhost scanning
- Job Control – Supports canceling, pausing, and resuming of tasks, inspired by Burp scanner
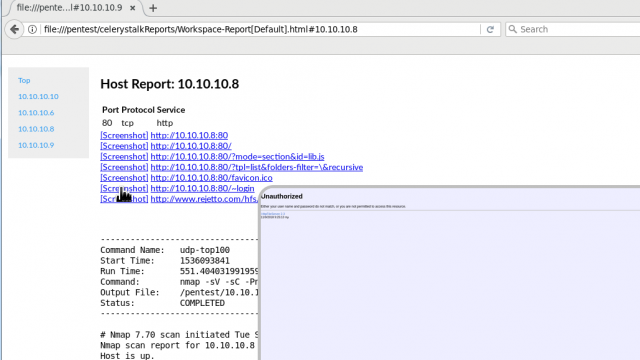
- Screenshots Automatically takes screenshots of every url identified via brute force (gobuster) and spidering (Photon)
Install/Setup
- Supported Operating Systems: Kali
- Supported Python Version: 2.x
You must install and run celerystalk as root
# git clone https://github.com/sethsec/celerystalk.git
# cd celerystalk/setup
# ./install.sh
# cd ..
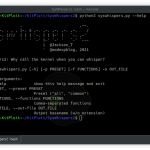
# ./celerystalk -hYou must install and run celerystalk as root
Using celerystalk – The basics
[CTF/HackTheBox mode] – How to scan a host by IP
# nmap 10.10.10.10 -Pn -p- -sV -oX tenten.xml # Run nmap
# ./celerystalk workspace create -o /htb # Create default workspace and set output dir
# ./celerystalk import -f tenten.xml # Import scan
# ./celerystalk db services # If you want to see what services were loaded
# ./celerystalk scan # Run all enabled commands
# ./celerystalk query watch (then Ctrl+c) # Watch scans as move from pending > running > complete
# ./celerystalk report # Generate report
# firefox /htb/celerystalkReports/Workspace-Report[Default.html] & # View report [Vulnerability Assessment Mode] – How to scan a list of in-scope hosts/networks and any subdomains that resolve to any of the in-scope IPs
# nmap -iL client-inscope-list.txt -Pn -p- -sV -oX client.xml # Run nmap
# ./celerystalk workspace create -o /assessments/client # Create default workspace and set output dir
# ./celerystalk import -f client.xml -S scope.txt # Import scan and scope files
# ./celerystalk subdomains -d client.com,client.net # Find subdomains and determine if in scope
# ./celerystalk scan # Run all enabled commands
# ./celerystalk query watch (then Ctrl+c) # Wait for scans to finish
# ./celerystalk report # Generate report
# firefox <path>/celerystalkReports/Workspace-Report[Default].html &# View report [URL Mode] – How to scan a a URL (Use this mode to scan sub-directories found during first wave of scans).
# ./celerystalk workspace create -o /assessments/client # Create default workspace and set output dir
# ./celerystalk scan -u http://10.10.10.10/secret_folder/ # Run all enabled commands
# ./celerystalk query watch (then Ctrl+c) # Wait for scans to finish
# ./celerystalk report # Generate report
# firefox <path>/celerystalkReports/Workspace-Report[Default].html &# View report Using celerystalk – Some more detail
- Configure which tools you’d like celerystalk to execute: The install script drops a config.ini file in the celerystalk folder. The config.ini script is broken up into three sections:
Service Mapping – The first section normalizes Nmap & Nessus service names for celerystalk (this idea was created by @codingo_ in Reconnoitre AFAIK).[nmap-service-names] http = http,http-alt,http-proxy,www,http? https = ssl/http,https,ssl/http-alt,ssl/http? ftp = ftp,ftp? mysql = mysql dns = dns,domain,domainDomain Recon Tools – The second section defines the tools you’d like to use for subdomain discovery (an optional feature):
[domain-recon] amass : /opt/amass/amass -d [DOMAIN] sublist3r : python /opt/Sublist3r/sublist3r.py -d [DOMAIN]Service Configuration – The rest of the confi.ini sections define which commands you want celerystalk to run for each identified service (i.e., http, https, ssh).
- Disable any command by commenting it out with a ; or a #.
- Add your own commands using [TARGET],[PORT], and [OUTPUT] placeholders.
Here is an example:
[http] whatweb : whatweb http://[TARGET]:[PORT] -a3 --colour=never > [OUTPUT].txt cewl : cewl http://[TARGET]:[PORT]/ -m 6 -w [OUTPUT].txt curl_robots : curl http://[TARGET]:[PORT]/robots.txt --user-agent 'Googlebot/2.1 (+http://www.google.com/bot.html)' --connect-timeout 30 --max-time 180 > [OUTPUT].txt nmap_http_vuln : nmap -sC -sV -Pn -v -p [PORT] --script=http-vuln* [TARGET] -d -oN [OUTPUT].txt -oX [OUTPUT].xml --host-timeout 120m --script-timeout 20m nikto : nikto -h http://[TARGET] -p [PORT] &> [OUTPUT].txt gobuster-common : gobuster -u http://[TARGET]:[PORT]/ -k -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/common.txt -s '200,204,301,302,307,403,500' -e -n -q > [OUTPUT].txt photon : python /opt/Photon/photon.py -u http://[TARGET]:[PORT] -o [OUTPUT] ;gobuster_2.3-medium : gobuster -u http://[TARGET]:[PORT]/ -k -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-lowercase-2.3-medium.txt -s '200,204,301,307,403,500' -e -n -q > [OUTPUT].txt - Run Nmap or Nessus:
- Nmap: Run nmap against your target(s). Required: enable version detection (-sV) and output to XML (-oX filename.xml). All other nmap options are up to you. Here are some examples:
nmap target(s) -Pn -p- -sV -oX filename.xml nmap -iL target_list.txt -Pn -sV -oX filename.xml - Nessus: Run nessus against your target(s) and export results as a .nessus file
- Nmap: Run nmap against your target(s). Required: enable version detection (-sV) and output to XML (-oX filename.xml). All other nmap options are up to you. Here are some examples:
- Create worksapce:
Option Description no options Prints current workspace create Creates new workspace -w Define new workspace name -o Define output directory assigned to workspace Create default workspace ./celerystalk workspace create -o /assessments/client Create named workspace ./celerystalk workspace create -o /assessments/client -w client Switch to another worksapce ./celerystalk workspace client - Import Data: Import data into celerystalk
Option Description -f scan.xml Nmap/Nessus xml - Adds all IP addresses from this file to hosts table and marks them all in scope to be scanned.
- Adds all ports and service types to services table.
-S scope.txt Scope file - Show file differences that haven’t been staged
-D subdomains.txt (sub)Domains file - celerystalk determines whether each subdomain is in scope by resolving the IP and looking for IP in the DB. If there is a match, the domain is marked as in scope and will be scanned.
Import Nmap XML file: ./celerystalk import -f /assessments/nmap.xml Import Nessus file: ./celerystalk import -f /assessments/scan.nessus Import list of Domains: ./celerystalk import -D <file> Import list of IPs/Ranges: ./celerystalk import -S <file> Specify workspace: ./celerystalk import -f <file> Import multiple files: ./celerystalk import -f nmap.xml -S scope.txt -D domains.txt - Find Subdomains (Optional): celerystalk will perform subdomain recon using the tools specified in the config.ini.
Option Description -d domain1,domain2,etc Run Amass, Sublist3r, etc. and store domains in DB - After running your subdomain recon tools celerystalk determines whether each subdomain is in scope by resolving the IP and looking for IP in the DB. If there is a match, the domain is marked as in scope and will be scanned.
Find subdomains: celerystalk subdomains -d domain1.com,domain2.com - Launch Scan: I recommend using the import command first and running scan with no options, however you do have the option to do it all at once (import and scan) by using the flags below. celerystalk will submit tasks to celery which asynchronously executes them and logs output to your output directory.
Option Description no options Scan all in scope hosts - Reads DB and scans every in scope IP and subdomain.
- Launches all enabled tools for IPs, but only http/http specific tools against virtualhosts
-t ip,vhost,cidr Scan specific target(s) from DB or scan file - Scan a subset of the in scope IPs and/or subdomains.
-s Simulation
Sends all of the tasks to celery, but all commands are executed with a # before them rendering them inert.Use these only if you want to skip the import phase and import/scan all at once -f scan.xml Import and process Nmap/Nessus xml before scan - Adds all IP addresses from this file to hosts table and marks them all in scope to be scanned.
Adds all ports and service types to services table.
-S scope.txt Import and process scope file before scan - Show file differences that haven’t been staged.
-D subdomains.txt Import and process (sub)domains file before scan - celerystalk determines whether each subdomain is in scope by resolving the IP and looking for IP in the DB. If there is a match, the domain is marked as in scope and will be scanned.
-d domain1,domain2,etc Find Subdomains and scan in scope hosts - After running your subdomain recon tools celerystalk determines whether each subdomain is in scope by resolving the IP and looking for IP in the DB. If there is a match, the domain is marked as in scope and will be scanned.
Scan imported hosts/subdomains
Scan all in scope hosts: ./celerystalk scan Scan subset of DB hosts: ./celerystalk scan -t 10.0.0.1,10.0.0.3 ./celerystalk scan -t 10.0.0.100-200 ./celerystalk scan -t 10.0.0.0/24 ./celerystalk scan -t sub.domain.com Simulation mode: ./celerystalk scan -sImport and Scan
Start from Nmap XML file: ./celerystalk scan -f /pentest/nmap.xml -o /pentest Start from Nessus file: ./celerystalk scan -f /pentest/scan.nessus -o /pentest Scan all in scope vhosts: ./celerystalk scan -f <file> -o /pentest -d domain1.com,domain2.com Scan subset hosts in XML: ./celerystalk scan -f <file> -o /pentest -t 10.0.0.1,10.0.0.3 ./celerystalk scan -f <file> -o /pentest -t 10.0.0.100-200 ./celerystalk scan -f <file> -o /pentest -t 10.0.0.0/24 Simulation mode: ./celerystalk scan -f <file> -o /pentest -s - Rescan: Use this command to rescan an already scanned host.
Option Description no option For each in scope host in the DB, celerystalk will ask if if you want to rescan it -t ip,vhost,cidr Scan a subset of the in scope IPs and/or subdomains. Rescan all hosts: ./celerystalk rescan Rescan some hosts ./celerystalk rescan-t 1.2.3.4,sub.domain.com Simulation mode: ./celerystalk rescan -s - Query Status: Asynchronously check the status of the tasks queue as frequently as you like. The watch mode actually executes the linux watch command so you don’t fill up your entire terminal buffer.
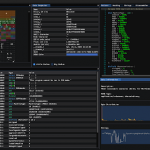
Option Description no options Shows all tasks in the defualt workspace watch Sends command to the unix watch command which will let you get an updated status every 2 seconds brief Limit of 5 results per status (pending/running/completed/cancelled/paused) summary Shows only a banner with numbers and not the tasks themselves Query Tasks: ./celerystalk query ./celerystalk query watch ./celerystalk query brief ./celerystalk query summary ./celerystalk query summary watch - Cancel/Pause/Resume Tasks: Cancel/Pause/Resume any task(s) that are currently running or in the queue.
Option Description cancel - Canceling a running task will send a kill -TERM
- Canceling a queued task* will make celery ignore it (uses celery’s revoke).
- Canceling all tasks* will kill running tasks and revoke all queued tasks.
pause - Pausing a single task uses kill -STOP to suspend the process.
- Pausing all tasks* attemps to kill -STOP all running tasks, but it is a little wonky and you mind need to run it a few times. It is possible a job completed before it was able to be paused, which means you will have a worker that is still accepting new jobs.
resume - Resuming tasks* sends a kill -CONT which allows the process to start up again where it left off.
Cancel/Pause/Resume Tasks: ./celerystalk <verb> 5,6,10-20 #Cancel/Pause/Resume tasks 5, 6, and 10-20 from current workspace ./celerystalk <verb> all #Cancel/Pause/Resume all tasks from current workspaces - Run Report: Run a report which combines all of the tool output into an html file and a txt file. Run this as often as you like. Each time you run the report it overwrites the previous report.
Create Report: ./celerystalk report #Create a report for all scanneed hosts in current workspace - Access the DB: List the workspaces, hosts, services, or paths stored in the celerystalk database
Option Description workspaces Show all known workspaces and the output directory associated with each workspace services Show all known open ports and service types by IP hosts Show all hosts (IP addresses and subdomains/vhosts) and whether they are in scope and whether they have been submitted for scanning paths Show all paths that have been identified by vhost -w workspace Specify a non-default workspace Show workspaces: ./celeryststalk db workspaces Show services: ./celeryststalk db services Show hosts: ./celeryststalk db hosts Show paths: ./celeryststalk db paths - Export DB: Export each table of the DB to a csv file
Option Description no options Export the services, hosts, and paths table from the default database -w workspace Specify a non-default workspace Export current DB: ./celerystalk db export Export another DB: ./celerystalk db export -w test
Usage
Usage:
celerystalk workspace create -o <output_dir> [-w workspace_name]
celerystalk workspace [<workspace_name>]
celerystalk import [-f <nmap_file>] [-S scope_file] [-D subdomains_file] [-u <url>]
celerystalk subdomains -d <domains> [-s]
celerystalk scan [-f <nmap_file>] [-t <targets>] [-d <domains>] [-S scope_file] [-D subdomains_file] [-s]
celerystalk scan -u <url> [-s]
celerystalk rescan [-t <targets>] [-s]
celerystalk query ([full] | [summary] | [brief]) [watch]
celerystalk query [watch] ([full] | [summary] | [brief])
celerystalk report
celerystalk cancel ([all]|[<task_ids>])
celerystalk pause ([all]|[<task_ids>])
celerystalk resume ([all]|[<task_ids>])
celerystalk db ([workspaces] | [services] | [hosts] | [vhosts] | [paths])
celerystalk db export
celerystalk shutdown
celerystalk interactive
celerystalk (help | -h | --help)
Options:
-h --help Show this screen
-v --version Show version
-f <nmap_file> Nmap xml import file
-o <output_dir> Output directory
-S <scope_file> Scope import file
-D <subdomains_file> Subdomains import file
-t <targets> Target(s): IP, IP Range, CIDR
-u <url> URL to parse and scan with all configured tools
-w <workspace> Workspace
-d --domains Domains to scan for vhosts
-s --simulation Simulation mode. Submit tasks comment out all commands
Examples:
Workspace
Create default workspace celerystalk workspace create -o /assessments/client
Create named workspace celerystalk workspace create -o /assessments/client -w client
Switch to another worksapce celerystalk workspace client2
Import
Import Nmap XML file: celerystalk import -f /assessments/nmap.xml
Import Nessus file: celerystalk import -f /assessments/scan.nessus
Import list of Domains: celerystalk import -D <file>
Import list of IPs/Ranges: celerystalk import -S <file>
Import multiple files: celerystalk import -f nmap.xml -S scope.txt -D domains.txt
Subdomain Recon
Find subdomains: celerystalk subdomains -d domain1.com,domain2.com
Scan
Scan all in scope hosts: celerystalk scan
Scan subset of DB hosts: celerystalk scan -t 10.0.0.1,10.0.0.3
celerystalk scan -t 10.0.0.100-200
celerystalk scan -t 10.0.0.0/24
celerystalk scan -t sub.domain.com
Simulation mode: celerystalk scan -s
Import and Scan
Start from Nmap XML file: celerystalk scan -f /pentest/nmap.xml
Start from Nessus file: celerystalk scan -f /pentest/scan.nessus
Scan subset hosts in XML: celerystalk scan -f <file> -t 10.0.0.1,10.0.0.3
celerystalk scan -f <file> -t 10.0.0.100-200
celerystalk scan -f <file> -t 10.0.0.0/24
celerystalk scan -f <file> -t sub.domain.com
Simulation mode: celerystalk scan -f <file> -s
Rescan
Rescan all hosts: celerystalk rescan
Rescan some hosts celerystalk rescan-t 1.2.3.4,sub.domain.com
Simulation mode: celerystalk rescan -s
Query Mode
All tasks: celerystalk query
Update status every 2s: celerystalk query watch
Show only 5 tasks per mode: celerystalk query brief
Show stats only celerystalk query summary
Show stats every 2s: celerystalk query summary watch
Job Control (cancel/pause/resume)
Specific tasks: celerystalk cancel 5,6,10-20
celerystalk pause 5,6,10-20
celerystalk resume 5,6,10-20
All tasks current worspace: celerystalk cancel all
celerystalk pause all
celerystalk resume all
Access the DB
Show workspaces: celeryststalk db workspaces
Show services: celeryststalk db services
Show hosts: celeryststalk db hosts
Show vhosts only celeryststalk db vhosts
Show paths: celeryststalk db paths
Export DB
Export current DB: celerystalk db export
Credit
This project was inspired by many great tools:
- https://github.com/codingo/Reconnoitre by @codingo_
- https://github.com/frizb/Vanquish by @frizb
- https://github.com/leebaird/discover by @discoverscripts
- https://github.com/1N3/Sn1per
- https://github.com/SrFlipFlop/Network-Security-Analysis by @SrFlipFlop
Thanks to @offensivesecurity and @hackthebox_eu for their lab networks
Also, thanks to:
- @decidedlygray for pointing me towards celery, helping me solve python problems that were over my head, and for the extensive beta testing
- @kerpanic for inspiring me to dust off an old project and turn it into celerystalk
- My TUV OpenSky team and my IthacaSec hackers for testing this out and submitting bugs and features












Add Comment